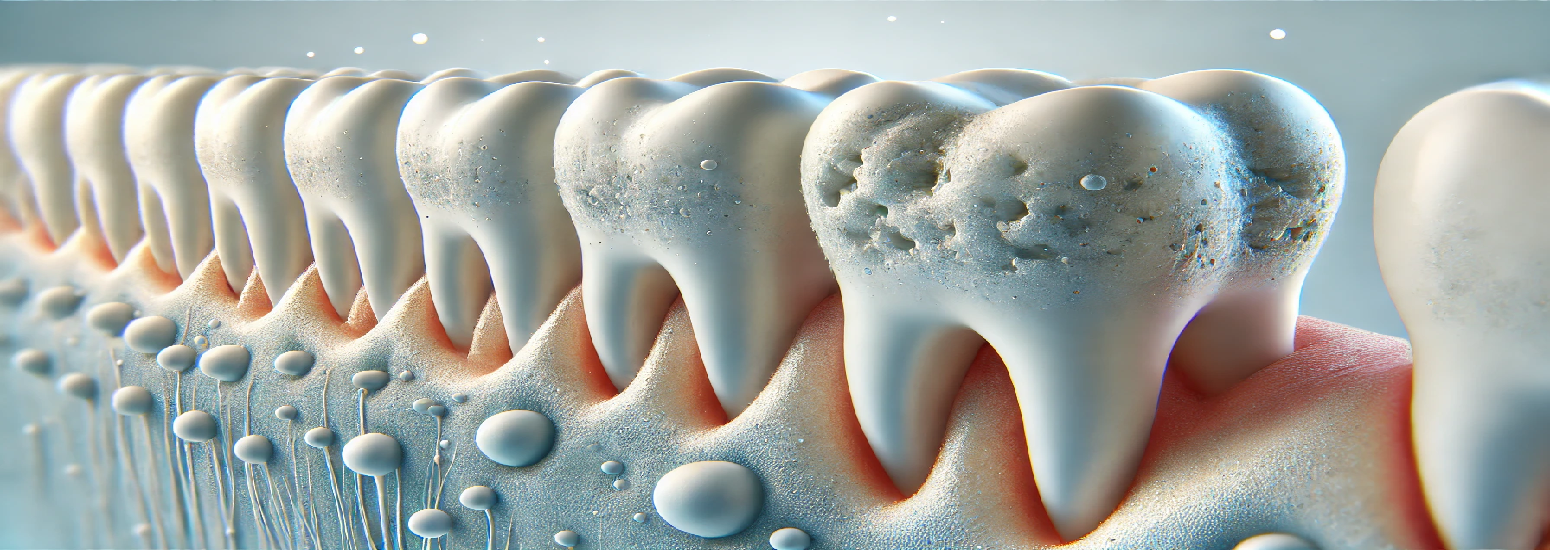
Dental erosion, also known as Acid erosion, is the irreversible loss of tooth structure due to chemical dissolution by acids not of bacterial origin. Dental erosion is the most common chronic disease of children ages 5–17, although it is only relatively recently that it has been recognized as a dental health problem. There is generally widespread ignorance of the damaging effects of acid erosion; this is particularly the case with erosion due to fruit juices, because they tend to be seen as healthy. Erosion is found initially in the enamel and, if unchecked, may proceed to the underlying dentin

Teeth Discoloration: Since the dentin of the tooth is exposed during tooth erosion, discoloration or yellowing of the teeth can occur.
Tooth Sensitivity: Sensitive teeth are very common symptoms of teeth erosion because the enamel that protects the teeth wears away.